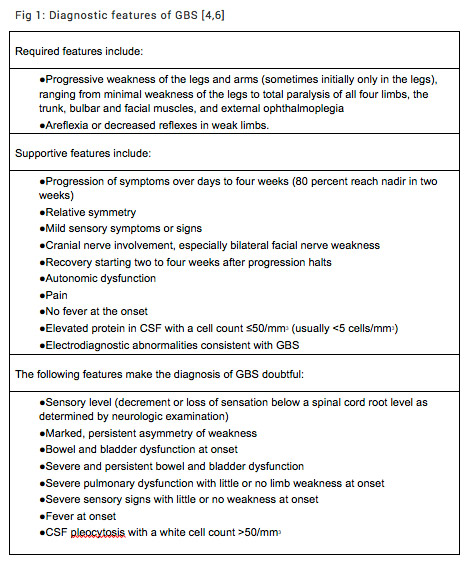
Guillain barre syndrome diagnosis criteria 695312-Guillain barre syndrome diagnosis criteria
Neurophysiological criteria in the diagnosis of different clinical types of GuillainBarre syndrome J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry , 79 ( 08 ) , pp 2 293 , /jnnp CrossRef View Record in Scopus Google ScholarGuillainBarré syndrome can be difficult to diagnose because several other conditions can cause similar symptoms A GP will refer you to a hospital specialist if they think you might have it or they are not sure what's causing your symptoms Examination A GP or specialist may ask about your symptoms, such as how long they've lasted and whether they're getting worse – muscle Guillain–Barré syndrome is a rare disorder in which the immune system goes into overdrive and the body attack its own nerves Common symptoms of the rare condition include weakness and tingling
Frontiers Zika Virus And Guillain Barre Syndrome Is There Sufficient Evidence For Causality Neurology
Guillain barre syndrome diagnosis criteria
Guillain barre syndrome diagnosis criteria-Criteria for the diagnosis of GuillainBarre syndrome are reaffirmed Electrodiagnostic criteria are expanded and specific detail added Asbury AK, Cornblath DR Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarr6 syndrome Ann Neurol 1990;27(suppl)S2 1S24 Diagnostic criteria for GuillainBard syndrome (GBS) were devised in 1978 at the request of the National GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is a rare but severe autoimmune disease and the usage of the Brighton criteria can be a source of great help in resourcelimited settings It encompasses all ages Late diagnosis of GBS can have a significant negative impact on the prognosis The Brighton criteria are used to assist in the diagnosis of GBS and help distinguish




Guillain Barre Syndrome Oncohema Key
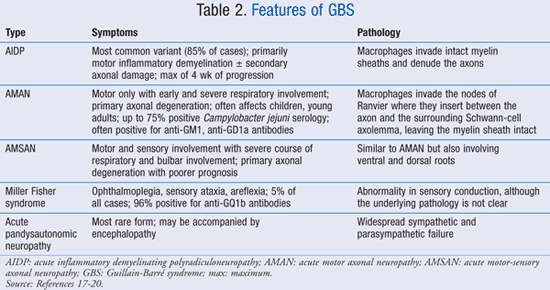
MillerFisher syndrome is a rare, acquired nerve disease that is a variant of GuillainBarré syndrome It is characterized by abnormal muscle coordination with poor balance and clumsy walking, weakness or paralysis of the eye muscles, and absence of the tendon reflexes Like GBS, symptoms may follow a viral illness Additional symptoms include generalized muscle weaknessCriteria for diagnosis of GuillainBarré syndrome Ann Neurol 1978;GuillainBarre syndrome is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathy that is classified according to symptoms and divided into axonal and demyelinating forms Twothirds of patients have a history of gastroenteritis or influenzalike illness weeks before onset of neurological symptoms Associated with
These symptoms usually affect both sides of the body at the same time Later symptoms The symptoms may3565 Asbury AK, Cornblath DR Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarré syndrome Ann Neurol 1990;GuillainBarré syndrome is the most common and most severe acute paralytic neuropathy, with about 100 000 people developing the disorder every year worldwide Under the umbrella term of GuillainBarré syndrome are several recognisable variants with distinct clinical and pathological features The severe, generalised manifestation of GuillainBarré syndrome with respiratory
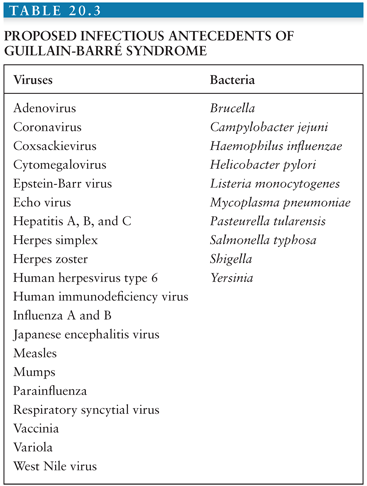
Syndrome and validation of Brighton criteria Brain 14, /brain/awt285 3 Goodfellow JA, Willison HJ GuillainBarré syndrome a century of progress Nat Rev Neurol 16, /nrneurol 4 Roodbol J, de Wit MY, van den Berg B, et al Diagnosis of GuillainBarré syndrome in children andGuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is viewed as a reactive, selflimited, autoimmune disease triggered by a preceding bacterial or viral infection Campylobacter jejuni, a major cause of bacterial gastroenteritis worldwide, is the most frequent antecedent pathogen It is likely that immune responses directed towards the infecting organisms are involved in the pathogenesis of GBS by Objective To report eight cases of sensory Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) Background The concept of sensory equivalent to ascending paralysis of GBS was raised in 1958, and the diagnostic criteria for a sensory loss and areflexia variant of GBS were proposed in 1981 However, clinical cases meeting these criteria have been relatively scarce Methods During a 13




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Zika Virus Infection In Colombia Nejm



Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathogenesis Diagnosis Treatment And Prognosis Nature Reviews Neurology
Criteria for diagnosis of GuillainBarré syndrome Ann Neurol 1978;3(6)565–566 4 Sejvar JJ, Baughman AL, Wise M, Morgan OW Population incidence of GuillainBarré syndrome aGuillainBarre syndrome is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathy that is classified according to symptoms and divided into axonal and demyelinating forms Twothirds of patients have a history of gastroenteritis or influenzalike illness weeks before onset of neurological symptoms Associated withSymptoms of GuillainBarré syndrome usually develop over hours or days and tend to start in your feet and hands before spreading to your arms and legs At first you may have numbness;




Epidemiology And Characteristics Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Northwest Of Iran Annals Of Saudi Medicine




Nerve Conduction Studies In Guillain Barre Syndrome Influence Of Timing And Value Of Repeated Measurements Sciencedirect
Diagnosis is descriptive, the criteria are ex pected to help neurologists and nomeurologists recognize the syndrome's diagnostic boundaries Drafting of the guidelines was precipitated in part by the increased27 SupplS21 Govoni V, Granieri E, Tola MR, et al The frequency of clinical variants of GuillainBarré syndrome in Ferrara, Italy J Neurol 1999; Diagnostic Criteria for GuillainBarre Syndrome (GBS) 26 July, 11 Guillermo Firman The GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) or LandryGuillainBarreStrohl syndrome, also known as postinfectious polyneuropathy or acute idiopathic polyneuritis, is an acute acquired, frequently severe, monophasic autoimmune illness of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) GBS




Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Diagnostic Criteria Necessary Criteria Download Table




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar
Of GuillainBarre Syndrome Diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarre syndrome have been established by an ad hoc NINCDS committee Because GuillainBarrt?Diagnostic criteria for GuillainBard syndrome (GBS) Barre syndrome occurs more frequently than by chance in were devised in 1978 at the request of the National the setting of preexisting illnesses such as Hodgkin's disease, zyxw Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disor lymphoma, or lupus erythematosus Many patients with ders and Stroke (NINCDS, now N I N D S GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) is the most common cause of acute, flaccid, neuromuscular paralysis in the United States GuillainBarre syndrome was first discovered more than a century ago Advances in the past century include investigating the immunemediated pathophysiology of the disease, recognizing the spectrum of presentations, advancing




Diagnostic Criteria For Guillain Barre Syndrome Download Table



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
GuillainBarré syndrome is an acute polyradiculoneuropathy with a variable clinical presentation Accurate diagnostic criteria are essential Criteria for the diagnosis of GuillainBarre syndrome Ann Neurol 1978~ 11 Asbury AK Diagnostic considerations in GuillainBarre spl)l5 syndrome Ann Neurol ( u p 12 Waterhouse J, Calum M Shanmugaratnam K, Powell J, eds Cancer incidence in five continents Vol 4 IARC Scientific publications No IS Lyon IARC, 13 Beghi E, Commonly used electrodiagnostic (EDX) criteria for GuillainBarré Syndrome (GBS) 1,2,3,4 rely solely on motor nerve conduction studies



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features Guillain Barre Syndrome In The Elderly Clinical Electrophysiological Therapeutic And Outcome Features
Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarre syndrome Ann Neurol 1990;27 S2 124 3 Van der Mechk FGA, Meulstee J, Vermeulen M, Kievit A Patterns of conduction failure in the GuillainBarri syndrome Brain 19; 4 Rhee EK, Sumner AJ A computer simulation of conduction block effects produced by actual block versus interphase cancellationAbstract Criteria for the diagnosis of GuillainBarré syndrome are reaffirmed Electrodiagnostic criteria are expanded and specific detail added Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarré syndrome Arthur K Asbury Dr, MD, Corresponding Author Department of Neurology, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA Department of Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare, but potentially fatal, immunemediated disease of the peripheral nerves and nerve roots that is usually triggered by infections The incidence of GBS



Lightning Learning Guillain Barre Syndrome Em3 East Midlands Emergency Medicine Educational Media



Gullian Barrie Syndrome Gbs
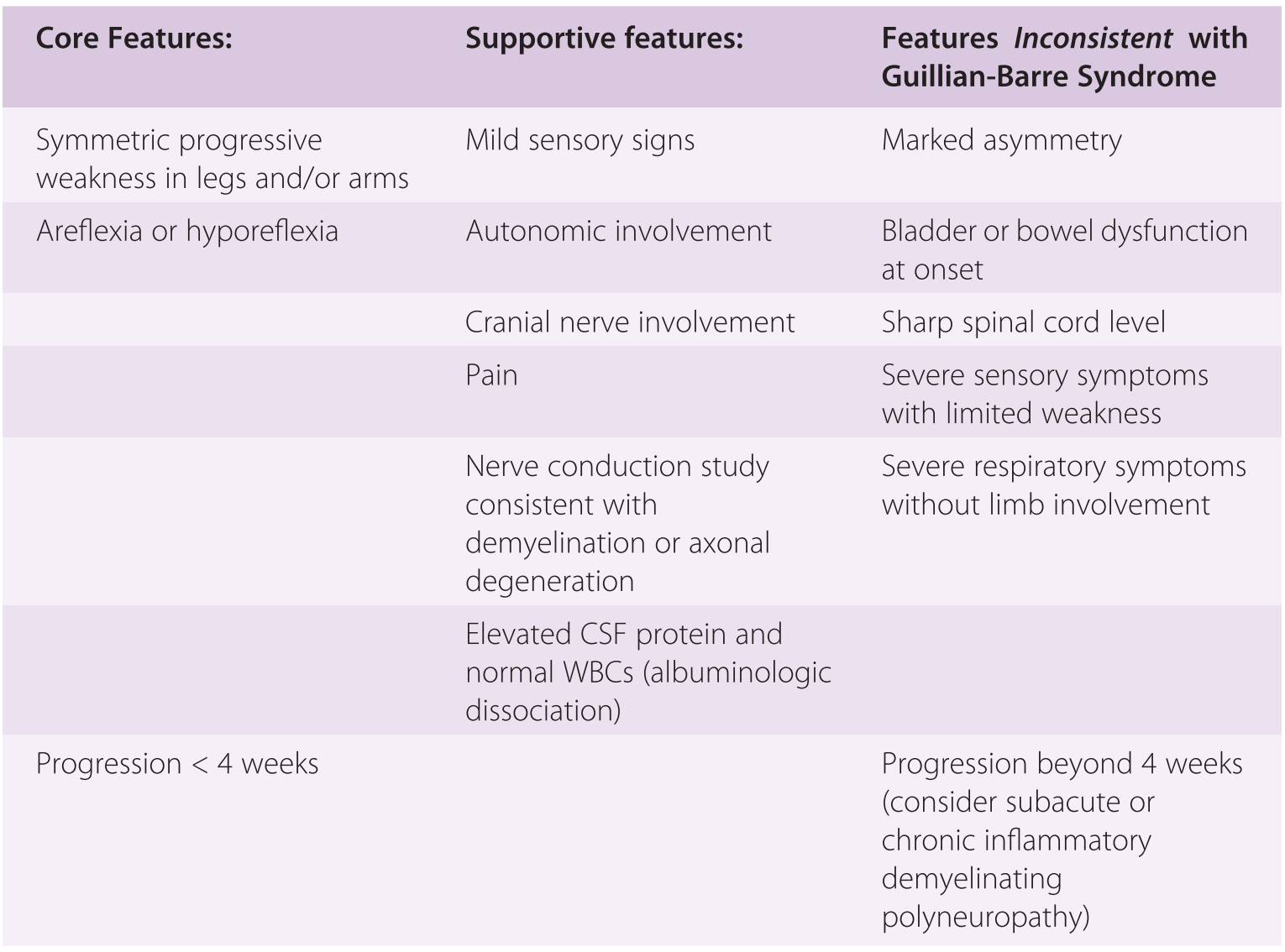
Diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarré syndrome include the presence of progressive weakness and areflexia, relative symmetry, mild sensory involvement, cranialIntroduction The diagnosis of GuillainBarré syndrome remains based on clinical characteristics and ancillary laboratory investigations, nearly one century after the namegiving publication of Georges Charles Guillain and JeanAlexandre Barré (Guillain et al, 1916)Accurate diagnostic criteria for GuillainBarré syndrome are important for clinical practice, especially in the early We aimed to evaluate the key diagnostic features of GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) in Malaysian patients and validate the Brighton criteria This was a retrospective study of patients presenting with GBS and Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) between 10 and 19 The sensitivity of the Brighton criteria was evaluated A total of 128 patients (95 GBS, 33 MFS) were included In




Guillain Barre Syndrome




Treatment Dilemmas In Guillain Barre Syndrome Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
NINDS Diagnostic Criteria for Guillain Barre Syndrome Features Required for GuillainBarré Syndrome • Progressive muscle weakness of more than one limb • Areflexia or hyporeflexia Features Supportive of Diagnosis • Progression of weakness for 24 weeks • Symmetric involvement, Mild sensory symptoms or signs, Cranial nerve involvement, Recovery The diagnostic criteria for GBS include progressive, relatively symmetrical weakness with decreased or absent myotatic reflexes For diagnosis, symptoms must reach maximal intensity within fourBackground Serial electrophysiology has been suggested as essential for accurate diagnosis in Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) However, whether more adapted electrophysiological criteria may allow a single study to be sufficient is unknown Methods We retrospectively reviewed records of 365 consecutive patients with GBS from Birmingham, UK, and Garches, France, admitted




Frontiers Zika Virus And Guillain Barre Syndrome Is There Sufficient Evidence For Causality Neurology



Guillain Barre Syndrome Oncohema Key
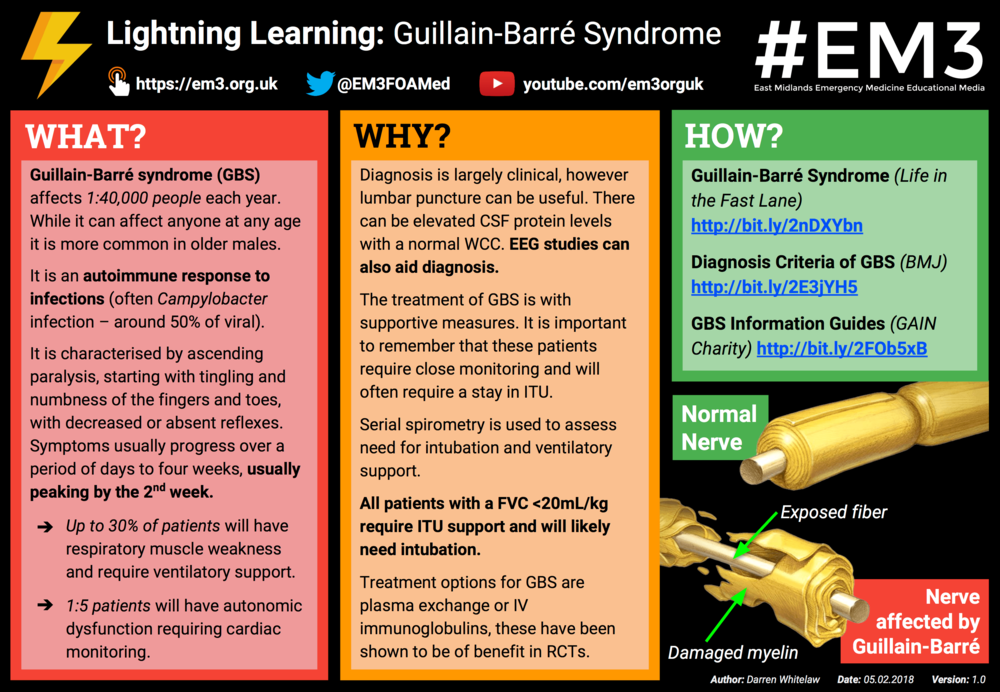
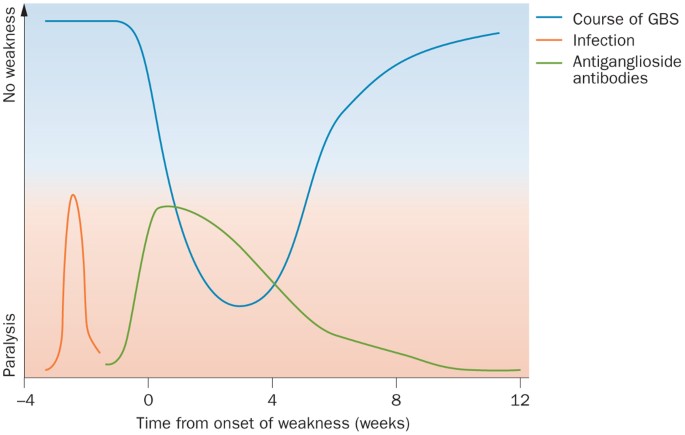
Guillain barré syndrome 1 GuillainBarré syndrome Dr Angelo Smith MD WHPL 2 GuillainBarre' 3 It has an annual incidence of 06 to 24 cases per 100,000 population and occurs at all ages and in both sexes With the marked decline in the incidence of polio, GuillainBarré syndrome is now the most common cause of acute flaccid paralysis in healthy people is an acuteProblems with balance and coordination;The Guillain–Barre´ syndrome (GBS) is a clinical diagnosis, supported by the results of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) 1 Recogni tion of GBS is important to start treatment and monitoring as soon as possible Accurate diagnostic criteria for GBS are also required to determine background incidence rates and to conduct vaccine safety




Sensory Disorders Clinical Neurology 8th Ed



Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathogenesis Diagnosis Treatment And Prognosis Nature Reviews Neurology
To describe the key diagnostic features of pediatric Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) and validate the Brighton criteria Retrospective cohort study of all children (Background Diagnostic criteria for the GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) have been available since 1978 Since then, several variants have been described More recently, a distinction has been made between pure motor forms, severe sensory forms, primary axonal and primary demyelinating varieties Associations of clinical characteristics, and specific infections and the presence of Box 1 Diagnostic criteria for Guillain–Barré syndrome This box lists the diagnostic criteria for Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) developed by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) 3 and subsequently modified in a review paper 6 We have added some features that cast doubt on the diagnosis, which were not mentioned in the original




Diagnosis And Scientific Physiotherapy Resources Facebook



Atypical Guillain Barre In The Emergency Department The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine
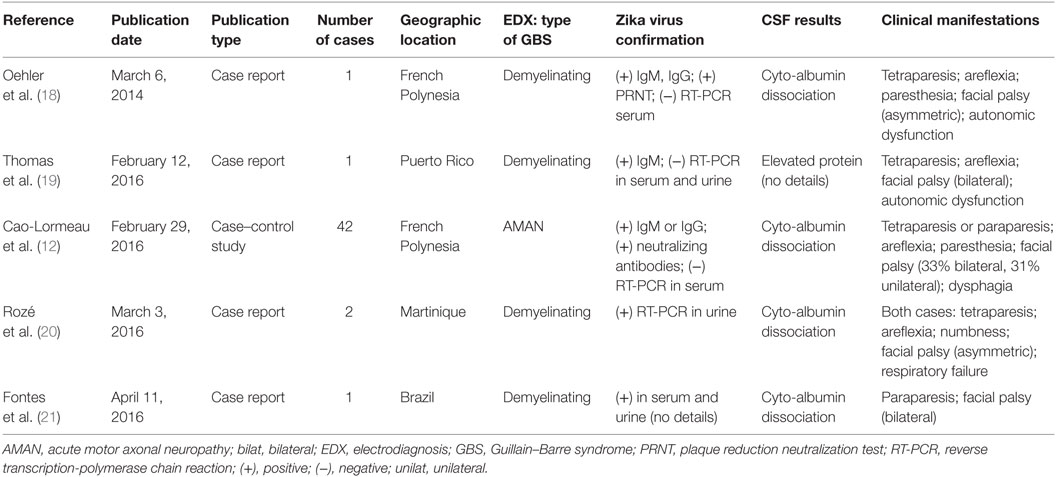
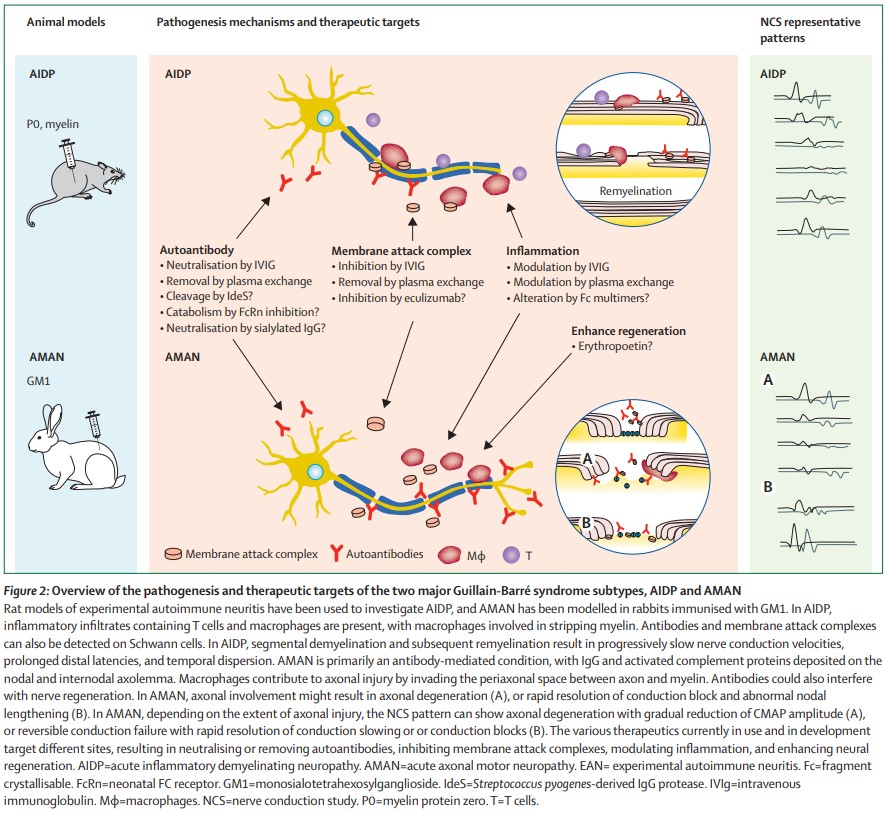
Abstract Guillain–Barr syndrome (GBS) is a rare, but potentially fatal, immune mediated disease of the peripheral nerves and nerve roots that is usually triggered by infections The incidence of GBS can therefore increase during outbreaks of infectious diseases, as was seen during the Zika virus epidemics in 13 in French Polynesia and 15 in Latin America Diagnosis andSeveral diagnostic criteriwt285 Epub 13 Oct 26 Authors Christiaan Fokke 1 , Bianca van den Berg, Judith Drenthen, Christa Walgaard, Pieter Antoon van Doorn, Bart Casper Jacobs Affiliation 1 1 The existing GuillainBarré syndrome diagnostic criteria exclude many variants, including GuillainBarré syndrome with preserved or brisk tendon reflexes97, 98 Although uncommon, this group of patients typically present with AMAN, an antecedent diarrhoeal illness, and antiganglioside antibodies 123 The recognition of GuillainBarré syndrome variants is




Pdf Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome And Validation Of Brighton Criteria Semantic Scholar




Pdf Pain In The Acute Phase Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Tomokazu Nakagawa Academia Edu
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapidonset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain often in the back along with muscle weakness, beginning in the feet and hands, often spreading to the arms and upper bodyDiagnostic criteria for the GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) have been available since 1978 Since then, several variants have been described More recently, a distinction hasIntroduction Diagnosis of Guillain Barre syndrome (GBS) is often made clinically Certain patient and disease characteristics can cause delays in diagnosis and managementMethods Observational retrospective study of fortyfour patients diagnosed with GBS either clinically, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, and/or by electrodiagnostic criteria at a teaching hospital



Guillain Barre Syndrome




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician
Clinical diagnostic criteria have in general been shown to be reliable in recently conducted clinical trials45 Electrodiagnostic tests may, however, in some cases be necessary in the differential diagnosis of GuillainBarre syndrome Moreover, in cases of clinically defined GuillainBarre syndrome, electrodiagnostic studies and, morespecificalGuillain–Barré syndrome is a onetime episode in more than 95% of cases 1 The generally accepted criteria for the diagnosis of Guillain–Barré syndrome include progressive, ascending weakness of more than two extremities, areflexia and numbness and tingling of fingers and toes 2 4 6 Other associated symptoms include mild sensory loss and elevated cerebrospinal fluidDiagnosis of GuillainBarre´ syndrome and validation of Brighton criteria Christiaan Fokke,1,2,3,4 Bianca van den Berg,1,5 Judith Drenthen,1,6 Christa Walgaard,1 Pieter Antoon van Doorn1 and Bart Casper Jacobs1,2 1 Department of Neurology, Erasmus Medical Centre Rotterdam, Rotterdam, 3000 CA, The Netherlands 2 Department of Immunology, Erasmus Medical Centre Rotterdam,




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Denmark Validation Of Diagnostic Co Clep




Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




The Guillain Barre Syndrome Nejm



Gbs Im Reference




Association Of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Polymorphism With Severity Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




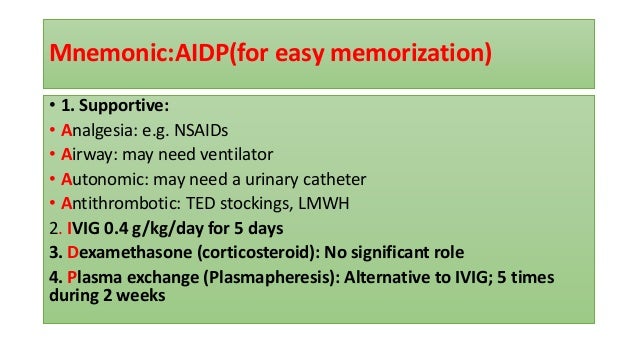
Treatment Guidelines For Guillain Barre Syndrome Meena A K Khadilkar S V Murthy J Ann Indian Acad Neurol




Therapeutic Plasma Exchange In Guillain Barre Syndrome And Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Sciencedirect
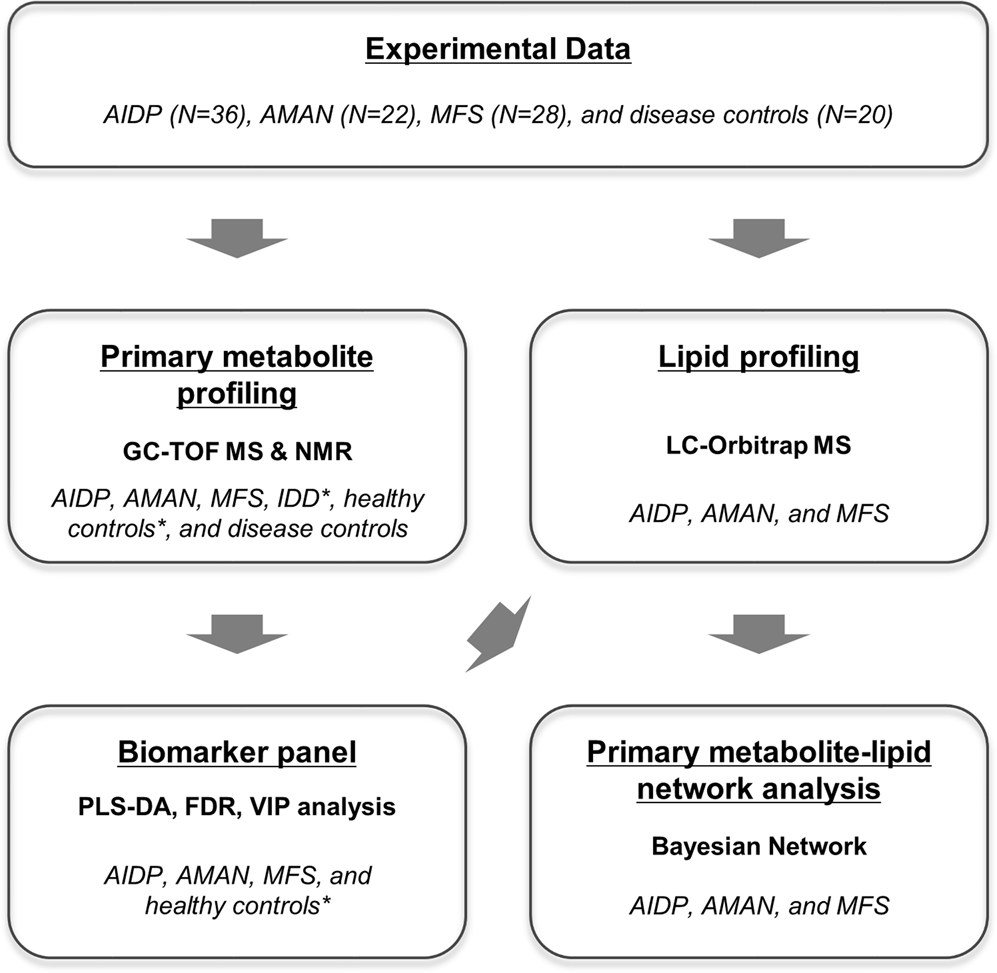



Integrative Metabolomics Reveals Unique Metabolic Traits In Guillain Barre Syndrome And Its Variants Scientific Reports




Guillain Barre Syndrome Oncohema Key



تويتر The Lancet على تويتر Diagnosis Of Classical Guillain Barre Syndrome Is Straightforward However Existing Diagnostic Criteria Have Limitations Meaning Variants Can Be Missed Geographical Variations Also Exist Subtypes Amp Access To



Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning
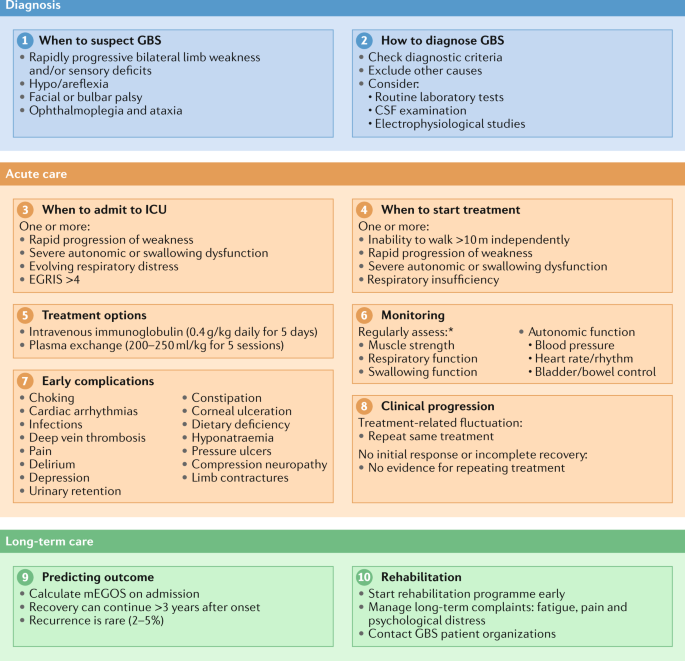



Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology




Ninds Diagnostic Criteria For Guillain Barre Syndrome Grepmed



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome




Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Children And Validation Of The Brighton Criteria Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science




Table 3 From Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome And Validation Of Brighton Criteria Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician



Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology




Peripheral Neuropathy Clinical Management Course February 12 07




Guillain Barre Syndrome Nejm



Manifestaciones Neurologicas De La Infeccion Por El Virus Zika




The Pathogenesis Of The Demyelinating Form Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Proteo Peptidomic And Immunological Profiling Of Physiological Fluids Molecular Cellular Proteomics



Nat Rev Neurology New Evidence Based Guidelines By Bart Jacobs And Colleagues Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps T Co Gg414gyy12 Openaccess Newfromnrneurology T Co Tolueqnaty Twitter




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Eastern China A Study Of 595 Patients Song European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning




Guillain Barre Syndrome Case 14 Neuromuscular Disease




Risk Of Psychiatric Disorders In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Nationwide Population Based Cohort Study Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Table 1 From Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Intact Thumb Reflex In Areflexic Guillain Barre Syndrome A Novel Phenomenon Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub



Guillain Barre Syndrome




Diagnostic Criteria For Guillain Barre Syndrome Features Required For Download Scientific Diagram




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician



Guillain Barre Syndrome



Plos One Hospital Admissions Transfers And Costs Of Guillain Barre Syndrome




Key Diagnostic Criteria And Brighton Case Definitions For Download Table




Validity Of Brighton Criteria In The Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs In Pakistan Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Southern China Retrospective Analysis Of Hospitalised Patients From 14 Provinces In The Area South Of The Huaihe River Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry




Treatment Guidelines For Guillain Barre Syndrome Meena A K Khadilkar S V Murthy J Ann Indian Acad Neurol



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationguillain Barre Syndrome Third Time S The Charm Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Table 6 From Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome And Validation Of Brighton Criteria Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mimics Tham 18 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Academy Of Neurology Webinar Youtube




Guillain Barre Syndrome




Review Article On Covid 19 And Guillain Barre Syndrome




Criteria For Guillain Barr6 Syndrome




View Image




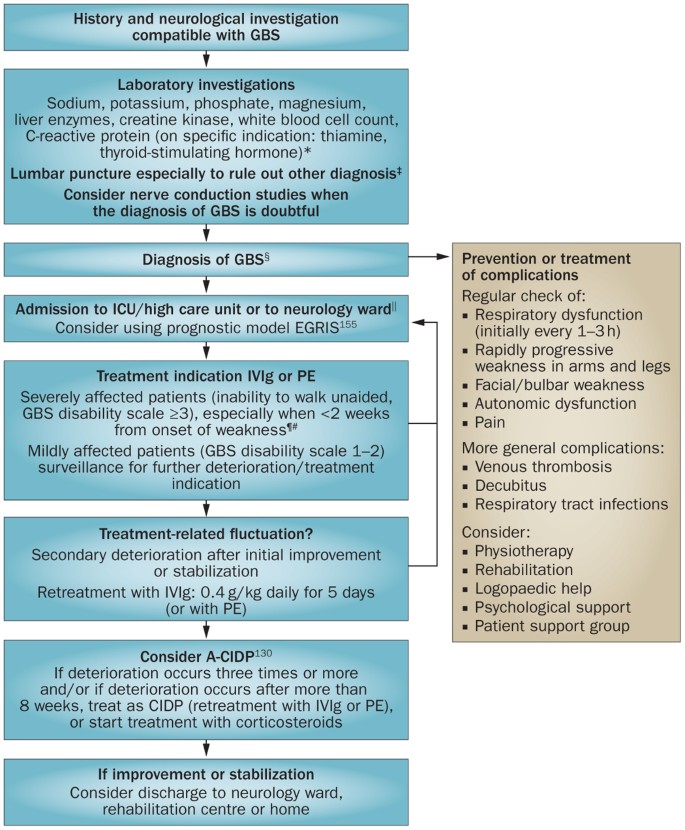
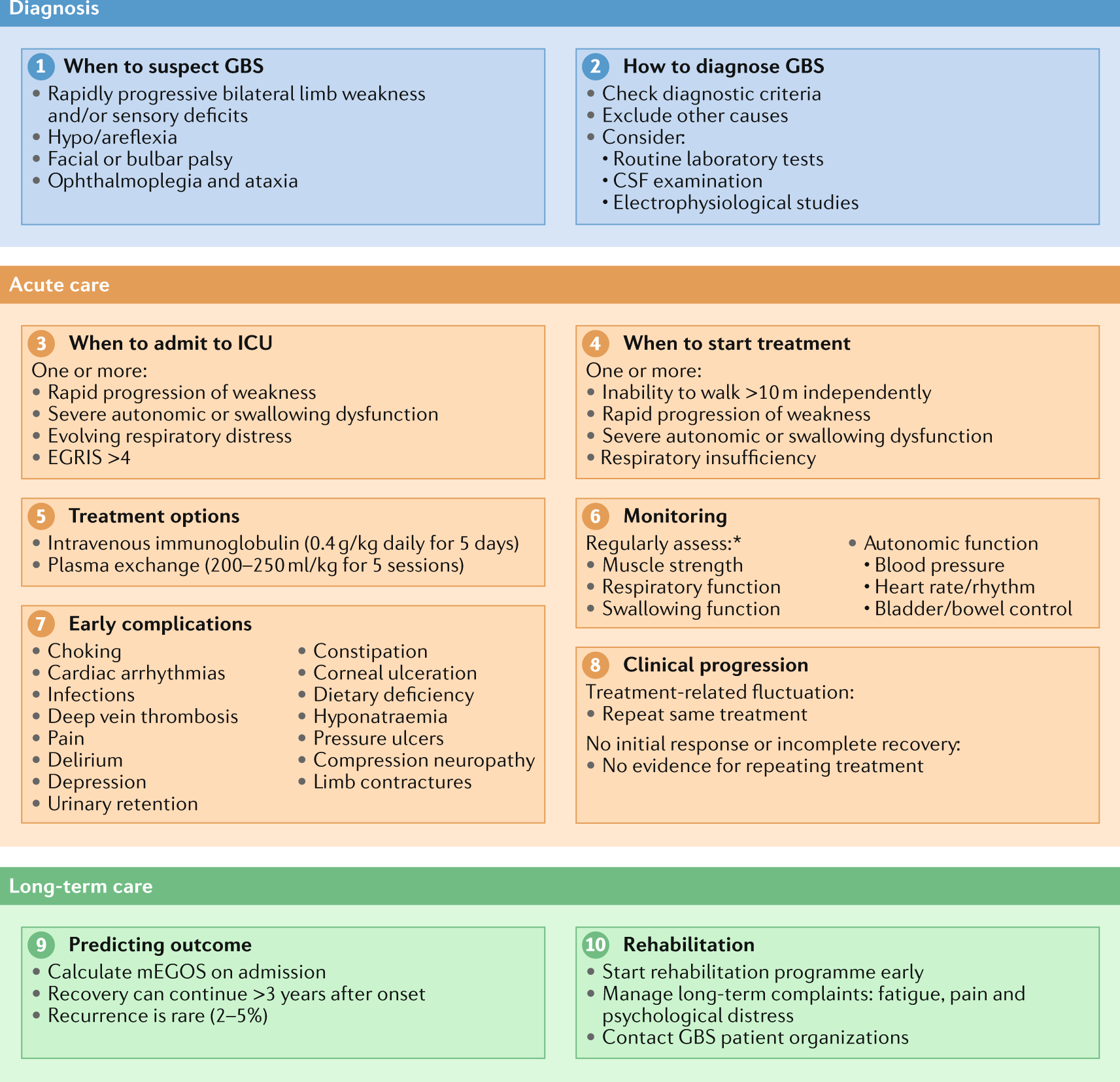
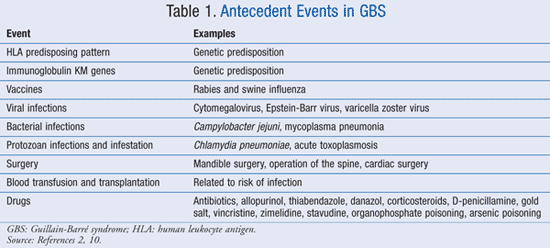
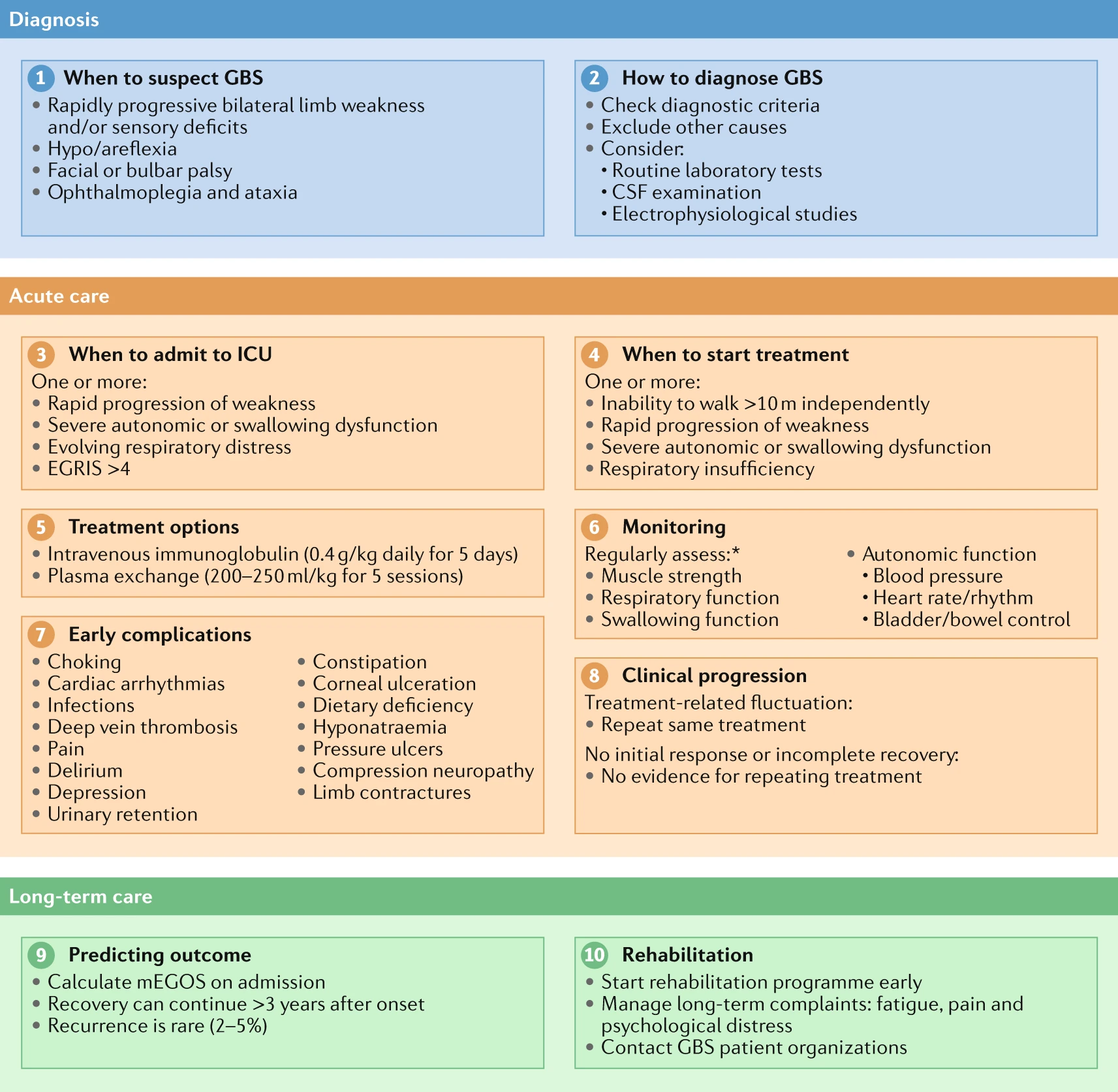
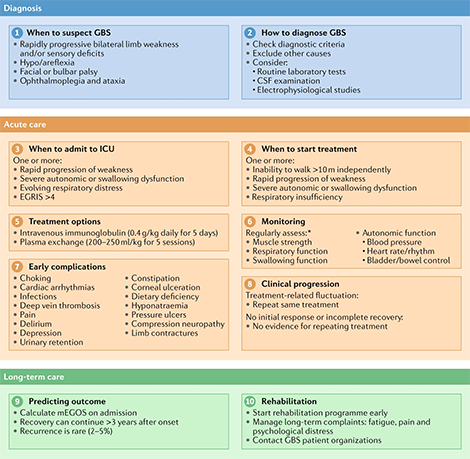
Mark Ramzy Do Emt P 10 Steps To Managing Guillain Barre Syndrome 1 When To Suspect 2 How To Diagnose 3 When To Admit To Icu 4 When To Start Treatment 5 Treatment Options 6 Monitoring 7 Early Complications



2



Nature Reviews Neurology Publishes Zikaplan Supported Landmark Paper Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Zikaplan




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Guillain Barre Syndrome And Its Variants As A Manifestation Of Covid 19 A Systematic Review Of Case Reports And Case Series Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Clinical And Electrophysiological Features Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Iran Sciencedirect



Gbs Patient




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Denmark Validation Of Diagnostic Co Clep



Clinical Characteristics Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Children Snpcar



Nature Reviews Neurology Publishes Zikaplan Supported Landmark Paper Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Zikaplan




Guillain Barre Syndrome Neupsy Key




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Diagnostic Criteria For Guillain Barre Syndrome Diagnosis Grepmed




References In Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Diagnostic Criteria For Guillain Barre Syndrome Ref Download Table




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Sars Cov 2 Nejm



1
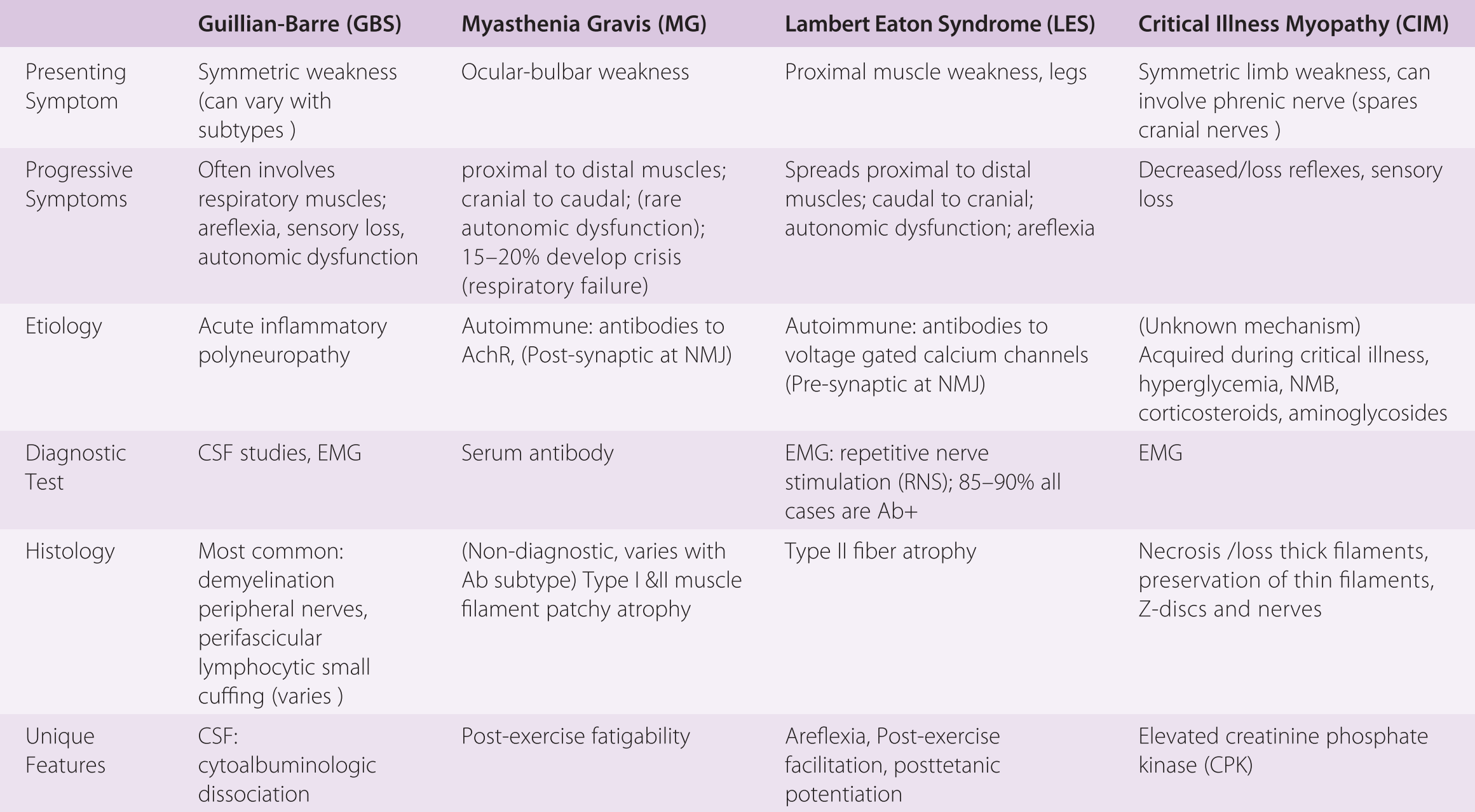



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning Netherlands




Clinical Features Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet Neurology
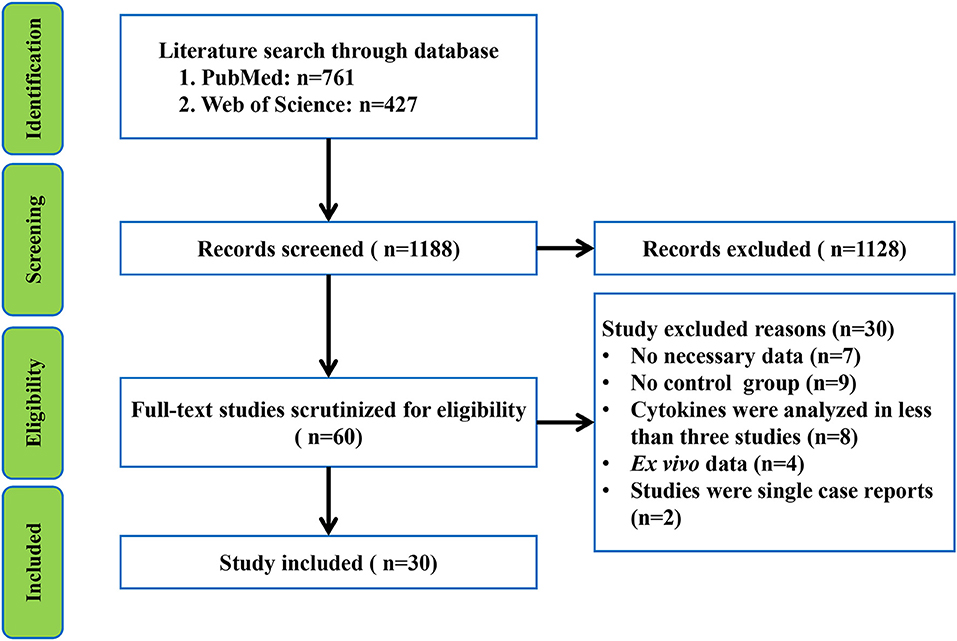



Frontiers Peripheral Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Levels In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Neuroscience
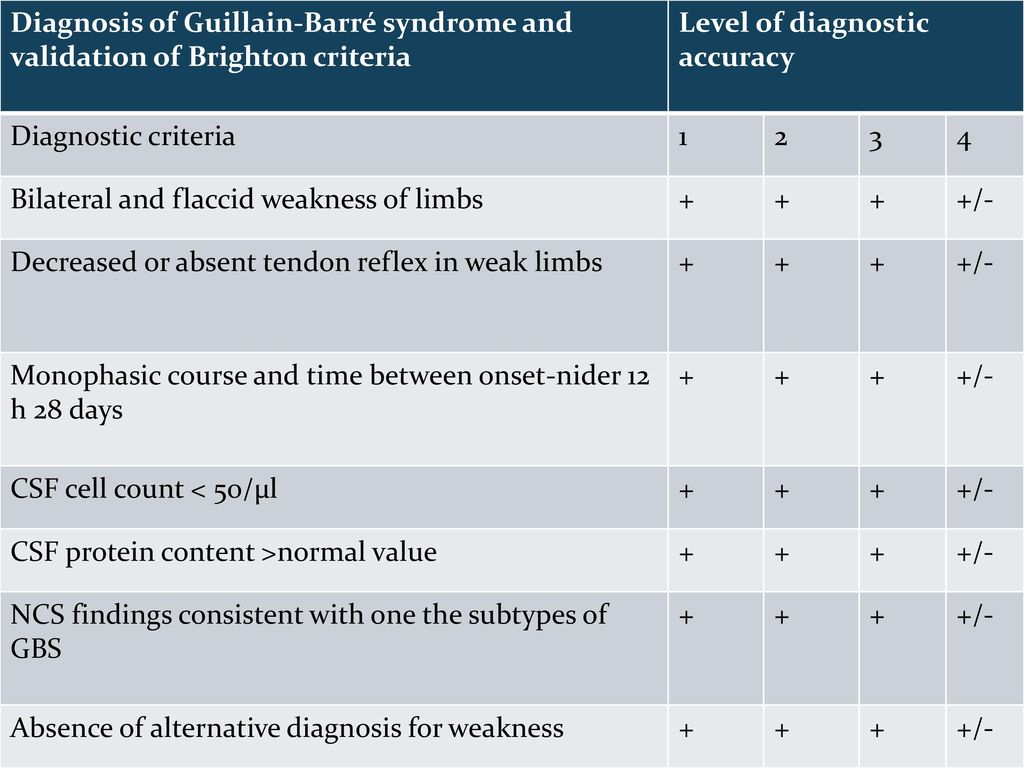



Guillain Barre Syndrome Ppt Download




Pdf Guillain Barre And Miller Fisher Syndromes New Diagnostic Classification Semantic Scholar



1




Guillain Barre Syndrome Rcemlearning




Prevalence And Outcomes Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Among Pediat Ndt



Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Emcrit Project
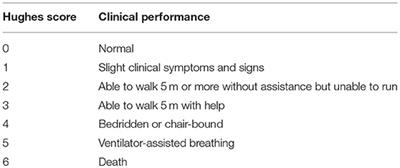



Frontiers Clinical Characteristics Of Intravenous Injection Of Monosialotetrahexosyl Ganglioside Sodium Related Guillain Barre Syndrome Neurology




Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Neuropedia Neuropathology




Clinical Variants Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Children Pediatric Neurology
コメント
コメントを投稿